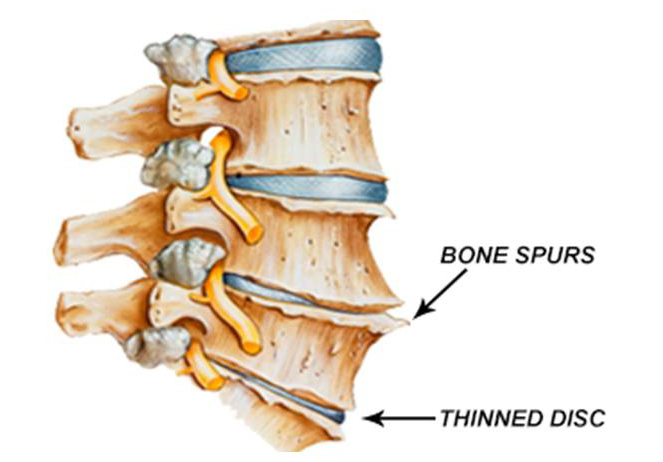
Spinal degeneration is a common complication among the elderly, but it is more common in obese people, in heavy physical work, and in spine injuries. Family backgrounds influence the development and development of osteoarthritis. The vertebrae are connected at three points.
First, in front of the spinal cord, the vetbrae are connected to each other by a disc. Second, at the back of the spinal cord, the vertebrae are joined by two small joints called facet joints. These facet joints with the intervertebral disc mobilize the spine (such as bending forward or backward or rotating to the sides). Osteoarthritis or spondylosis means the destruction of these three connecting areas on the surface of the vertebral body and the joints of the vertebrae or facet. Any curvature of the spine (scoliosis) causes imbalance of pressure to the joints and is effective in the development of osteoarthritis.
The most common type of spinal arthritis is osteoarthritis or degenerative arthritis .
تیترهای مهم این مقاله
Symptoms
Lumbar spine osteoarthritis usually causes axial pain in the spine, which is especially felt early in the morning and when waking up and relieves over time. Prolonged activity can exacerbate the symptoms of spinal spondylosis. With the development of degeneration, fine bone mass (osteophytes) is formed and enlarged, and if it develops within the canal, it presses and stimulates the nerve roots, causing diffuse pain, such as sciatica pain in the limbs.
Etiology
Age: More common in the fourth decade of life.
Sex: Women is about twice of men.
Injury: such as accidental injuries, sports accidents, or occupational injuries. Inheritance: It is possible to inherit joint deformities …
Overweight: Overweight causes pressure on the joints.
Diagnosis
Physical examination is of great importance.
Imaging Tests : Imaging tests provide the physician with complete information about the spinal canal including:
X-ray: To evaluate infection or bone mass
Computed tomography: Used for more bony evaluation.
MRI: Used to examine soft tissues including discs, ligaments, spinal cord and nerves.
Nerve and muscle function test (EMG&NCV):It is used to determine the physiological function of the nerves and muscle.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the spine
The treatment of lumbar spine osteoarthritis varies depending on the extent of the patient’s symptoms. The therapies are step by step, and if the patient does not respond appropriately to each treatment step, more sophisticated methods are used. The basis of osteoarthritis treatment is noninvasive procedures and the most important principle of soft tissue strengthening around the lumbar spine is to include:
Weight loss: Weight loss is difficult in patients with worn joints. However, losing weight can also be a factor in reducing pain. By reducing weight by 5 kg or more, the fastest joints will experience less stress and this can reliably reduce pain.
Rest: Rest should only be relative and not to include heavy movements or pressures on the waist, and no more.
Lumbar Brace: Temporary closure of the brace or belt is only recommended in very advanced cases of spondylosis associated with canal stenosis, and long-term use may weaken the spine muscles, leading to greater transfer of trauma and more advanced degeneration process.
Medications : Medications are used to relieve symptoms in the acute phase as well as to restore muscle strength and relaxation, including: muscle relaxants (peripheral and central), anti-inflammatory analgesics and in severe cases can be limited usage of narcotic drugs. In the non-acute phase of spondylosis, combined soy and avocado medications can also be used to prevent the progression and recovery of arthritic lesions.
Non-Invasive Treatments
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy uses a combination of passive methods and exercises to strengthen muscular structure and corrective movements. Passive therapeutic modalities such as ice / heat, ultrasound and electrical stimulation reduce pain and spasms in a patient with arthritis. The patient with arthritis learns exercises to increase flexibility and range of motion by increasing his or her muscles strength. Patients should not worry about switching to this treatment, even patients with pain and movement problems benefit from isometric exercises.
- Massage and Manipulation: The basis of these techniques performed by hand also strengthens the muscular structure of the tissues around the vertebrae.
- High Power Laser: Using high power pulse laser will increase cellular energy and repair damaged tissues and prevent the progression of arthritis.
Interventional treatments
Interventional procedures are performed by a pain specialist under the guidance of X-ray (fluoroscopy) or ultrasound in the operating room.
- Diagnostic and therapeutic injections : Injections into the spinal column such as combined steroids and topical anesthetics in the epidural space and injections into the intervertebral facet joints in a patient with spondylosis can cause Anti-inflammation effect of the arthritic area. They are also injected into the iterveetebral foramen of spinal canal. Radiofrequency in these areas can also be used for long-term changes in addition to injections. Other methods can be referred to as radiofrequency, ozone therapy, PRP injection, orthokine, etc., which have been described in detail elsewhere.