تیترهای مهم این مقاله
Neuralgic and neuropathic pain
Neuralgic and neuropathic pains are vague or sharp quality that occur in one or more nerve pathways and their causes may be trauma, irritation, or viruses, but in many cases their etiology is unknown.
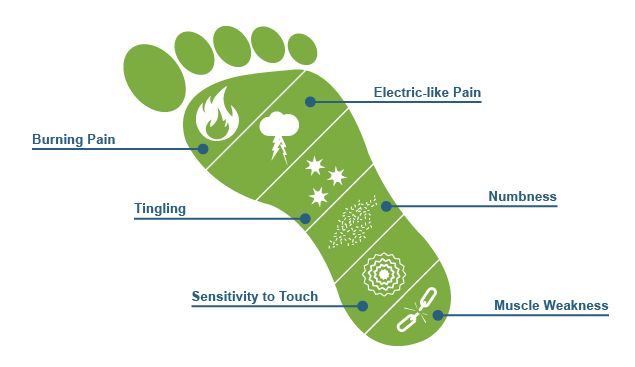
Neuralgic pains usually begin after the age of 40 and become more common in the elderly. Pain may have an area of burning sensation that is accompanied by sharp pain. These pains range from a few seconds to minutes and can range from several days to several weeks. At intervals of painful attacks, the affected area can show extreme reaction and sensitivity to any relatively mild contact or pain. Even stimuli that are not normally painful may cause pain (hyperalgesia, hyperesthesia). These kinds of pains do not conflict with life, but they severely affect one’s performance and can cause depression and anxiety to the extent that some people commit suicide.
Types of neuralgic and neuropathic pains
Neuralgia :
Trigeminal nerve neuralgia is the most common neuralgia, which is a severe, sharp pain similar to that of electrical on one side of the face, often stimulated by talking, chewing or brushing teeth. There is also a type of nerve pain called glossopharyngeal neuralgia that is characterized by recurrent attacks of severe pain in the back of the throat, tonsils, middle ear and tongue base. These attacks can be exacerbated by movements such as talking or swallowing food. In some cases this problem is extremely distressing. Another type of nerve pain is the pain in the back of the head(occiput) that usually radiates to the back of the ears into the scalp. Intercostal nerve neuralgia is also felt in the rib cage.
Diabete :
In diabete , high blood sugar, in addition to the involvement of vessels and organs, causes sensory and motor nerve fibers in the upper and lower limbs, called diabetic neuropathy, causing burning sensations and impaired sensation of movement. Touch and balance. The so-called neuropathy, glove and sock form means that these conflicts, such as wearing gloves or socks, begin to move farther away from the fingers.
Shingles :
The shingles virus causes nerve fibers that cause burning pain and neuropathic pain, which begins with contact with the affected area or with actions such as sneezing and coughing. This pain may persist for weeks, months, or sometimes years after all symptoms and symptoms of the virus have resolved.
CRPS :
Hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system causes limb swelling, hair loss and severe burning pains, which can cause limb dysfunction. This problem usually arises after injury to the area and requires blockage of the sympathetic zone associated with the pathology.
Postoperative pain :
Injury to the optic nerve and visceral nerve fibers in the area of surgery can cause burning pain in these areas that require therapeutic intervention.
Other neuropathic pain :
Neuropathic pain can also occurs in a variety of areas with unknown causes, which should be managed and treated by a specialist in the area of pain if not responding to routine treatment.
Treatment of neuralgic pain
Pharmacological treatment
For the treatment of neurological pain, the first line of treatment usually includes medications that relieve symptoms. The type of medicine your doctor prescribes depends on the type of nerve pain and the severity of its symptoms. The drugs used include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics, tricyclic antidepressants, anti-convulsants and more….
Nerve block
Doctors can use a nerve block if taking the medication cannot reduce nerve pain. In this case, some of the topical anesthetic can be injected into the area for a limited period of time to relieve pain. A long-term approach may include blocking the involved nerve with the use of neurolytic drugs. These drugs destroy the nerve tissue in the affected area and help relieve pain.
Interventional treatment
Interventional or minimally invasive treatments are performed by a pain specialist in the operating room under the guidance of fluoroscopy or ultrasound.
Minimally invasive treatments include radiofrequency of nerve, neural block, modulation of sympathetic plexus activity, intrathecal pump, spinal cord stimulator, and so on. That is explained in other sections.
Thank you for reading the article “Neurologic Pain” to the End
Dr. Kazemi Pain Fellowship